Do you know how your skin’s “deeper layers” protect your body?
Let’s Talk Skin
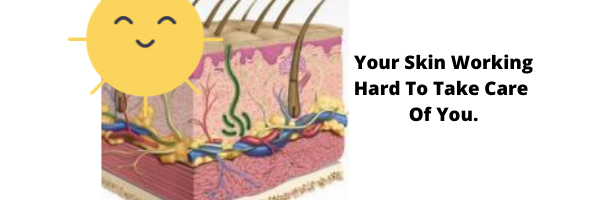
Understanding a bit about your skin anatomy will help you make some better decisions about limiting sun on your bare skin. We can’t see the deeper layers of our skin, and it is hard to appreciate what they do.
We do have decisions to make about how we protect our skin from too much sun. Sun blocking clothing is an easy way to protect yourself. All you have to do to get the benefit of this protection is to wear the clothing.
How you decide to protect yourself from the sun will guide your skin health. Will you try to do all the protection with sunscreen, or will you add some UPF clothing to help out? What about a few better choices in your lifestyle?
Your skin varies in thickness from .05 mm to 6 mm. The thinnest layer is located on your eyelids! Your palms and soles of the feet are where your skin is the thickest.
Altogether, your skin accounts for approximately one-sixth of your total body weight. So, your largest organ in (or, actually, on) your body is your skin.
However, your skin gets one-third of your cardiac output when you are at rest. That is an impressive amount of your heart’s work, just for your skin.
Does this help remind you of what you already knew from the classroom? It is important to protect yourself from the dangers of too much sun.
This is one thing we can control, our skin’s sun exposure.
We can control this part by wearing clothing. The lifestyles we choose make a difference. Ch
Coices about when you are out in the sun will be a place we can all start. Be careful about exposing your skin during the midday when the sun is the highest and strongest.
Your Skin’s Deeper Layers Explained
As you know, your skin is composed of two layers, the epidermis, and the dermis.
Under your dermis is your subcutaneous tissue.
The deeper structures, located under the subcutaneous tissues include muscle, bone as well as the important structures that support more functions of your skin.
The inner layers of your skin that are alive and growing are called the malpighian layer.
What happens in the malpighian layer?
This is where the dead cells that we can see are grown. This malpighian layer is in direct contact with the dermis, where the blood feeds and supports it.
The malpighian layer is our focus of attention when talking about sun blocking clothing. Here is where the sun damages our skin as it is turning tan.
The Deeper Layers Of Your Skin.
Your malpighian layer is itself divided into these layers:
- The Basal layer. In direct contact with the dermis. This is where basal cell carcinoma (cancer) starts.
- Right on top of the basal layer you will find the spinous layer.
- Then, above the spinous layer is the granular layer.
Above the granular layer is the stratum corneum. The stratum corneum is the outer layer of dead cells. These are the cells that we see and identify as our skin. Or your skin on the surface of your body.
Your cells in this stratum corneum layer are filled with a protein called keratin.
Keratin is a very interesting protein because it is tough. Think horns, hair, hoofs, fingernails, and feathers. These all gain their strength from keratin.
The same stuff that, makes up your fingernails? This is the stuff that actually forms your visible skin (just in a much thinner and more flexible layer).
That is what makes your skin so tough. In parts of your body that get a lot of wear, like your palms and feet, the stratum corneum layer is thicker to handle the wear.
Now, About Your Tan Cells
Another kind of cell lives among your basal cells in the malpighian layer. This cell is called a melanocyte.
Melanocytes produce melanin.
Melanin is a pigment that allows your skin to tan. So, the melanocytes are actually where your tan comes from.
Not only do your melanocytes produce your tan? They are also responsible for the form of cancer called melanoma. Every time you expose your skin to the sun you are stimulating the melanocytes to produce melanin.
Every time you also risk the danger of stimulating melanoma tumors in your body. When is the one time too many?
When will your melanoma be stimulating a tumor along with your tan? Is this the time in the sun that will result in DNA that can no longer reproduce normal skin cells? Your skin’s deeper layers can only protect you so far. You have to help.
Melanoma is caused by UV radiation damage to melanocytes. Repeated exposure to UV can cause cancerous mutations.
Dermis Layer Of Your Skin’s Deeper Layers
Your dermis layer is where the action is to help your skin function as it was designed to do.
Here in the dermis, you will find your sweat glands, hair follicles. (Did you know that each of your hair follicles has it’s own tiny little muscle? This little muscle is what makes your “hair can stand on end”!).
Your nerve endings also live here in your dermis.
There are several different types of nerve endings:
- Heat sensitive: lets you know when you are hot or the surface of a stove is hot, or if the sun is burning your skin.
- Cold sensitive: alerts you that you are cold. That surfaces you touch or get close to are cold or frozen. Helps you pull away.
- Pressure sensitive: Calls your attention to places on your skin that are feeling pressure. From minor isses like your hairband is too tight, to being hit to the bruising point. Again allowing you to protect yourself.
- Itch sensitive: Allowing you to know that something is happening on your skin.
- Pain sensitive: Allowing you to know that there is a reason to check your skin. Stop what is causing pain before it damages your skin.
These different nerve endings allow you to sense the world.
They also help you protect yourself from burns, punctures, and the like by warning you when something is damaging your skin.
The Epidermis
The epidermis is your direct wire to the world. The way your body reacts to the world around us. It has to work properly to allow your skin to stay healthy.
There are 2 has two main layers:
The living inner layer.
Then the outer layer, the one that is dead.
The dead skin cells of the outer layer are what we can actually see. They are constantly flaking off by new cells in their push outward. Your body needs a certain amount of cells to operate properly. They have their orders from the DNA to reform and keep reforming.
When the skin cell receives damage and can no longer reproduce correctly, the new cells that grow are often different. They may not lay down as they did before the injury.
Some types of injury end with a scar on the surface of your skin. If the DNA receives damage to the point it no longer knows when to stop growing? You then have skin cancer.
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cells. Skin cells will keep growing because they reproduce too quickly, the life cycle of the cell they are replacing is not over. There are too many skin cells. There is no place for them to be.
The result will be sores and tumors on your skin.
The shut off part of the skin cells DNA is missing. In the case of skin cancer, it is usually because of sun damage. Repeated sun damage.
Sami’s Take on Your Skin’s “Deeper Layers”
We know our body is a complex group of organs that keep us going. Often our body does such a good job that we forget that we have a part in this staying healthy thing too.
I thought I could continue to have fun in the sun and not worry about any consequences. Well, let me tell you, that is not true. I should have been worrying from the first.
With what we know at this point about how to help our skin stay healthy, you can hope to live a life without skin cancer worries. However, you will need to do your part of the protection cycle.
Are you recognizing some habits that will get you in trouble with your skin? When we are unaware of the danger in the actions we are taking and the decisions we are making, these bad habits can slip in.
With some information and better options, you can have fun in the sun and stay safe. What can you do to improve your lifestyle to be healthier?
